Heart Rhythm Disturbances in Cats: Understanding Arrhythmias and Their Implications

Heart rhythm disturbances, or arrhythmias, in cats refer to abnormal patterns of heartbeats. While it might sound alarming, not all arrhythmias are necessarily dangerous. However, understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and management of these disturbances is crucial for cat owners to ensure the well-being of their feline friends.
Types of Arrhythmias:
-
Bradycardia: This refers to a slow heart rate, where the heart beats too slowly.
-
Tachycardia: This is a fast heart rate, where the heart beats too quickly.
-
Atrial Fibrillation: This irregular rhythm occurs in the upper chambers of the heart (atria), leading to rapid, disorganized contractions.
-
Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening condition where the heart's lower chambers (ventricles) quiver and can't pump blood, leading to collapse and sudden cardiac arrest.
-
Premature Contractions: Early heartbeats, either in the atria (premature atrial contractions) or ventricles (premature ventricular contractions), can disrupt the regular rhythm.
Causes of Arrhythmias:
-
Heart Diseases: Conditions like cardiomyopathy, valvular disorders, or congenital heart defects can lead to arrhythmias.
-
Electrolyte Imbalance: Abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium in the bloodstream can affect the heart's electrical conduction system.
-
Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism can cause tachycardia, while hypothyroidism can cause bradycardia.
-
Toxicity: Certain substances like medications, plants, or chemicals can lead to arrhythmias if ingested by cats.
Symptoms of Arrhythmias:
-
Lethargy: Cats might appear weak or tired.
-
Difficulty Breathing: Rapid breathing or open-mouth breathing can occur.
-
Collapse: In severe cases, cats might collapse, especially during physical activity.
-
Coughing: Some arrhythmias, particularly those related to heart disease, can cause coughing.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
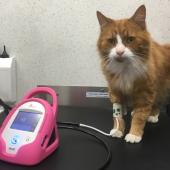
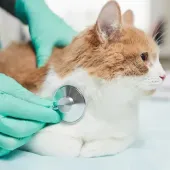
A veterinarian can diagnose arrhythmias through physical examination, listening to the heart using a stethoscope, and possibly performing electrocardiography (ECG or EKG). The treatment varies based on the underlying cause and severity. Medications to regulate heart rhythm, manage heart disease, or correct electrolyte imbalances are common treatments. In severe cases, hospitalization and intensive care might be necessary, especially if the cat is experiencing ventricular fibrillation.
Prevention and Management:
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for early detection, especially for senior cats. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding toxic substances can contribute to overall heart health. Cat owners should also be cautious about administering any medications without veterinary supervision, as some drugs can trigger arrhythmias.
In conclusion, while heart rhythm disturbances in cats can be concerning, early detection, appropriate management, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve a cat's quality of life. Cat owners play a crucial role in observing their pets for any unusual symptoms and seeking prompt veterinary care if any concerns arise.